Cadence

Overview¶
Cadence is a multi-tenant orchestration framework that helps with managing workflows. It scales horizontally to handle millions of concurrent executions from various customers. Cadence Open Sources uses docker compose to run their server, and uses Apache CassandraⓇ as its default backend dependency. Using docker compose, users are able to also use Cadence with MySQL, PostgreSQL, Statsd+Graphite, and Elasticsearch.
Prerequisites¶
- You should have an Astra account
- You should Create an Astra Database
- You should Have an Astra Token
Note
This runbook was written using Mac OS Monterey but it will also work with Windows. Any Windows-specific instructions will be noted as such.
Installation and Setup¶
✅ 1. Setup Astra¶
- In your Astra database, create two new keyspaces called "cadence" and "cadence_visibility". You will be using both of these in the next steps.
- Make sure to create an Astra token with Admin Role
- Get your Database ID
Find your Database ID in one of two ways
- Navigate to your your database and get the last ID in the URL:
https://astra.datastax.com/org/.../database/xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx - Copy and paste the Datacenter ID without the trailing
-1from the Regions section of your Astra Dashboard.
✅ 2. Cadence Pre-setup¶
- Clone this GitHub repository
- Navigate to your cloned repository and using your preferred text editor (e.g. VisualStudio or Sublime), update the .env file with your Astra Token and Astra Database ID that you obtained above.
✅ 3. Cadence Schema Migration to Astra DB¶
For this step, you will set up the keyspaces you created earlier in the Astra prerequisites (cadence and cadence_visibility). You will be using cadence-cassandra-tool which is part of the Temporal repo and it relies on schema definition.
- Navigate to your cloned
cadence-astra-cql-proxydirectory - Run the following commands to initialize the keyspaces that we created through Astra. Note that there are two sets of commands, one for
cadencekeyspace and one forcadence_visibilitykeyspace:
docker-compose -f docker-compose-schema.yaml run cadence \
-ep cqlproxy-cadence -k cadence setup-schema -v 0.0
docker-compose -f docker-compose-schema.yaml run cadence \
-ep cql-proxy -k cadence update-schema -d schema/cassandra/cadence/versioned/
docker-compose -f docker-compose-schema.yaml run cadence \
-ep cql-proxy -k cadence_visibility setup-schema -v 0.0
docker-compose -f docker-compose-schema.yaml run cadence \
-ep cql-proxy -k cadence_visibility update-schema -d schema/cassandra/visibility/versioned/
Once the process is completed, you should see a message similar to this:
2022/04/05 21:50:24 Starting schema setup, config=&{SchemaFilePath: InitialVersion:0.0 Overwrite:false DisableVersioning:false}
2022/04/05 21:50:24 Setting up version tables
2022/04/05 21:50:25 Setting initial schema version to 0.0
2022/04/05 21:50:25 Updating schema update log
2022/04/05 21:50:26 Schema setup complete
...
2022/04/05 22:13:16 ---- Done ----
2022/04/05 22:13:16 Schema updated from 0.32 to 0.33, elapsed 1.4960138s
2022/04/05 22:13:16 All schema changes completed in 32.5941245s
2022/04/05 22:13:16 UpdateSchemeTask done
Great! Your schemas have been migrated with Astra DB.
Confirm your tables exist in Astra
You can double-check to make sure the correct tables have been created by querying your database in Astra DB’s CQL Console.
Run DESC tables; in both your cadence and cadence_visibility keyspaces. You should see there are tables loaded in that were created by the schema migration with cadence-cassandra-tool.
token@cqlsh> use cadence;
token@cqlsh:cadence> desc tables;
history_node schema_version tasks history_tree
domains_by_name_v2 executions domains events
cluster_config queue queue_metadata schema_update_history
token@cqlsh:cadence> use cadence_visibility ;
token@cqlsh:cadence_visibility> desc tables;
open_executions closed_executions_v2 closed_executions
schema_update_history schema_version
✅ 4. Run Docker Compose¶
In this step, the docker-compose.yaml file is already provided for you in the cadence-astra-cql-proxy repo. This file creates different docker containers to run Temporal server. The persistence layer is configured for you to connect with cql-proxy, and it should pull your Astra credentials from when you set it earlier.
services:
cql-proxy:
container_name: cqlproxy
image: datastax/cql-proxy:v${CQL_PROXY_VERSION}
...
environment:
- ASTRA_TOKEN=${ASTRA_TOKEN}
- ASTRA_DATABASE_ID=${ASTRA_DATABASE_ID}
- HEALTH_CHECK=true
Now you can run the docker-compose command to start up Cadence:
✅ 5. Test and Validate¶
You can test your connection and play with your Cadence cluster with these instructions. Using Cadence’s Command Line tool, you will be able to interact with your local Temporal server.
- Create a domain
samples-domainby running the following command. You should see the success message once the domain is created:
- Clone the sample project repository to your machine. Navigate to this project and run make to build all the projects.
- Once this is complete, you can start by running the sample Hello World project by following the instructions in that repository.
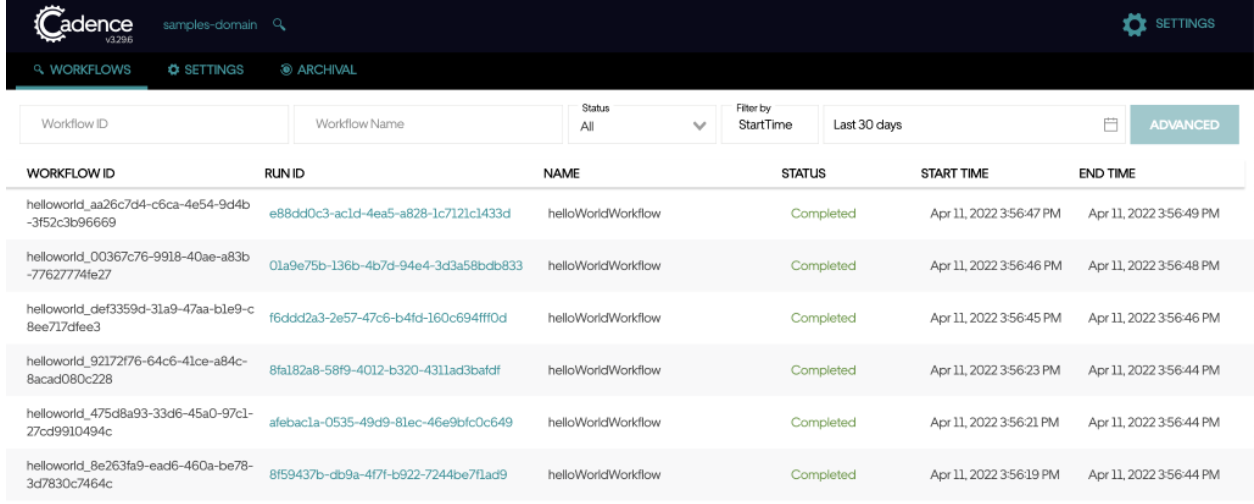
Once you have this all running, you should be able to see your workflows reflect on both the Cadence UI and Astra UI. You can see the domain on the top left is samples-domain, the domain we created, as well as the Status of each workflow as “Completed”.