Apache Beam

Overview¶
Apache Beam is an open-source, unified programming model for batch and streaming data processing pipelines which simplifies large-scale data processing dynamics. Thousands of organizations around the world choose Apache Beam due to its unique data processing features, proven scale, and powerful yet extensible capabilities.
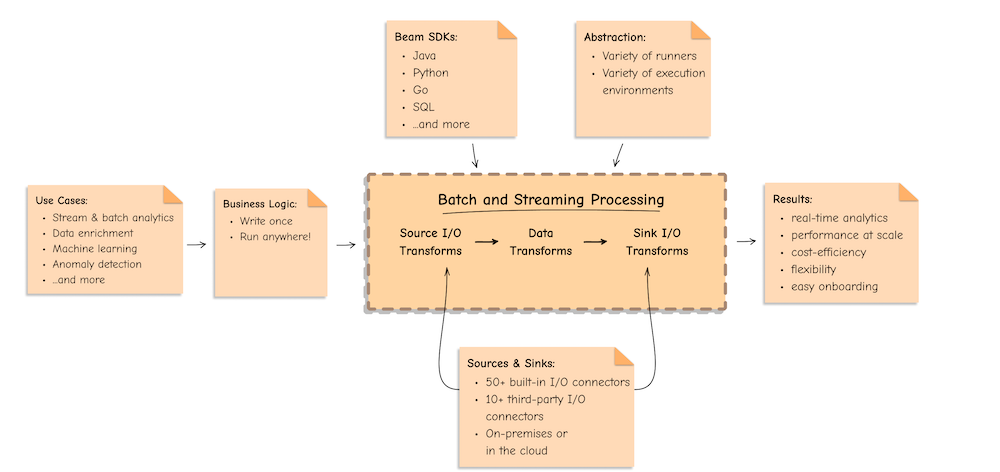
Main Concepts
-
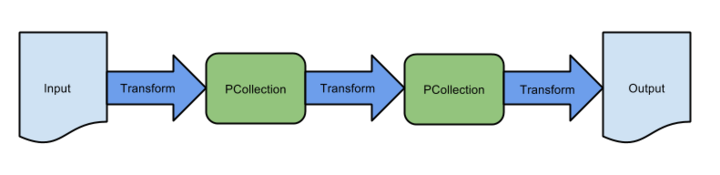
Pipeline: APipelineencapsulates your entire data processing task, from start to finish. This includes reading input data, transforming that data, and writing output data. All Beam driver programs must create a Pipeline. When you create the Pipeline, you must also specify the execution options that tell the Pipeline where and how to run. -
PCollection: APCollectionrepresents a distributed data set that your Beam pipeline operates on. The data set can be bounded, meaning it comes from a fixed source like a file, or unbounded, meaning it comes from a continuously updating source via a subscription or other mechanisms. Your pipeline typically creates an initial PCollection by reading data from an external data source, but you can also create a PCollection from in-memory data within your driver program. From there, PCollections are the inputs and outputs for each step in your pipeline. -
PTransform: APTransformrepresents a data processing operation, or a step, in your pipeline. Every PTransform takes one or more PCollection objects as input, performs a processing function that you provide on the elements of that PCollection, and produces zero or more output PCollection objects. -
Input and Output so called
I/O transforms: Beam comes with a number of “IOs” - library PTransforms that read or write data to various external storage systems.
I/O Connectors
Apache Beam I/O connectors provide read and write transforms for the most popular data storage systems so that Beam users can benefit from natively optimised connectivity. With the available I/Os, Apache Beam pipelines can read and write data to and from an external storage type in a unified and distributed way.
Integration with DataStax Astra is inspired by the built-in
CassandraIOandPulsarIOconnectors. This integration leverages a newAstraIOconnector.
Runners
A runner in Apache Beam is responsible for executing pipelines on a particular processing engine or framework, such as Apache Flink or Google Cloud Dataflow. The runner translates the Beam pipeline into the appropriate format for the underlying engine, manages job execution, and provides feedback on job progress and status.

Prerequisites¶
- You should have Java11+, Maven, and Git installed
- You should have an Astra account
- You should Create an Astra Database
- You should Have an Astra Token
- You should Download your Secure Connect Bundle
Setup your JAVA Development environment
- Install Java Development Kit (JDK) 8+
Use java reference documentation targetting your operating system to install a Java Development Kit. You can then validate your installation with the following command.
- Install Apache Maven (3.8+)
Samples and tutorials have been designed with Apache Maven. Use the reference documentation top install maven validate your installation with
Setup Datastax Astra DB
- Create your DataStax Astra account:
- Create an Astra Token
An astra token acts as your credentials, it holds the different permissions. The scope of a token is the whole organization (tenant) but permissions can be edited to limit usage to a single database.
To create a token, please follow this guide
The Token is in fact three separate strings: a Client ID, a Client Secret and the token proper. You will need some of these strings to access the database, depending on the type of access you plan. Although the Client ID, strictly speaking, is not a secret, you should regard this whole object as a secret and make sure not to share it inadvertently (e.g. committing it to a Git repository) as it grants access to your databases.
It is handy to have your token declare as an environment variable (replace with proper value):
- Create a Database and a keyspace
With your account you can run multiple databases, a Databases is an Apache Cassandra cluster. It can live in one or multiple regions (dc). In each Database you can have multiple keyspaces. In the page we will use the database name db_demo and the keyspace keyspace_demo.
You can create the DB using the user interface and here is a tutorial. You can also use Astra command line interface. To install and setup the CLI run the following:
curl -Ls "https://dtsx.io/get-astra-cli" | bash
source ~/.astra/cli/astra-init.sh
astra setup --token ${ASTRA_TOKEN}
To create DB and keyspace with the CLI:
- Download the Secure Connect Bundle for current database
A Secure Connect Bundle contains the certificates and endpoints informations to open a mTLS connection. Often mentionned as scb its scope is a database AND a region. If your database is deployed on multiple regions you will have to download the bundle for each one and initiate the connection accordingly. Instructions to download Secure Connect Bundle are here
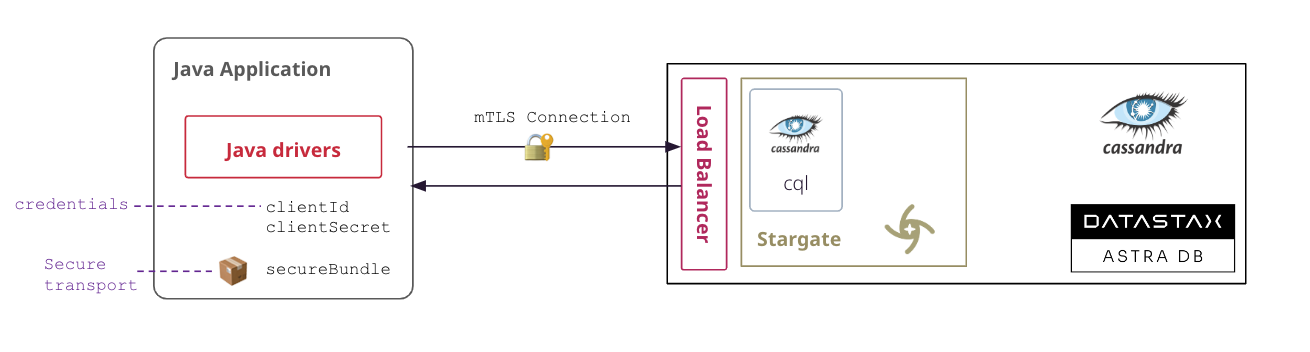
You can download the secure connect bundle from the user interface and here is a tutorial. You can also use Astra command line interface.
Installation and Setup¶
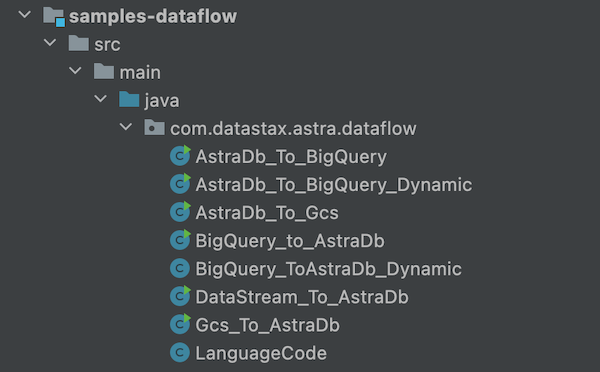
- Clone the Repository with sample flows. The different flows are distributed in 2 different modules.
sample-beamscontains flows that do not interact with Google Cloud solutions and will be run with a direct runner.sample-dataflowscontains flows that could be executed.
- Navigate to the repository and build the project with maven.
More on the maven project setup locally
- Clone the Repository with
AstraIOand sample flows
- Build the project with maven
The different flows are distributed in 2 different modules:
sample-beamscontains flows that do not interact with Google Cloud solutions and will be run with a direct runner.
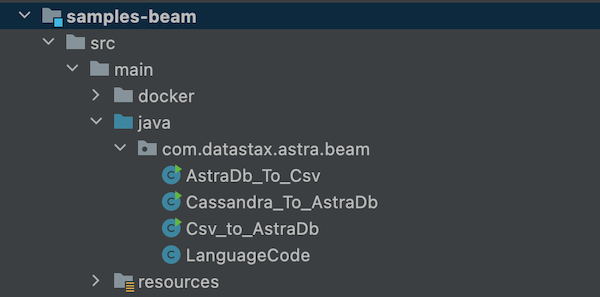
sample-dataflowscontains flow that could be executed
Examples¶
1. Import a CSV File¶
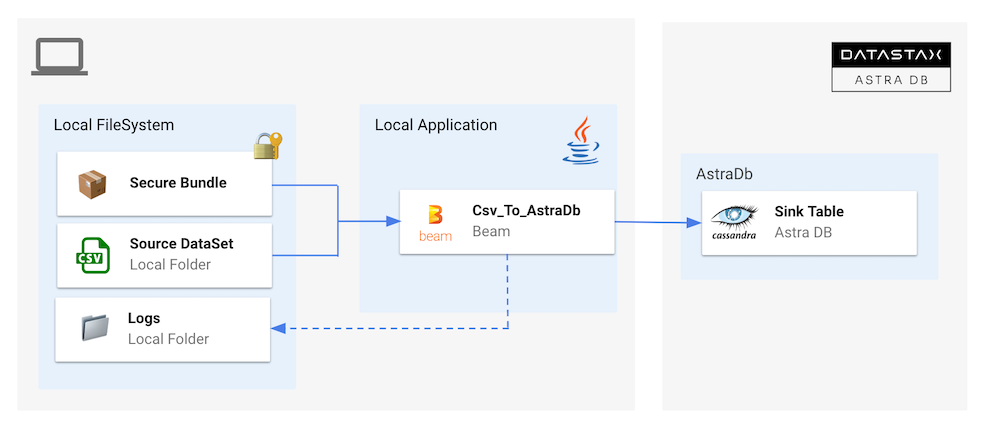
In this flow a
CSVfile is parsed to populate a table with same structure in Astra. The mapping from CSV to the table is done manually. The dataset is a list of languages.
- Access folder
samples-beamin the project.
- Setup Environment variables
# Database name (use with CLI)
export ASTRA_DB=<your-db-name>
# Keyspace name
export ASTRA_KEYSPACE=<your-keyspace-name>
# Path of local secure connect bundle
export ASTRA_SCB_PATH=<your-secure-connect-bundle>
# Astra Token starting by AstraCS:...
export ASTRA_TOKEN=<your-token>
- Run Beam pipeline
mvn clean compile exec:java \
-Dexec.mainClass=com.datastax.astra.beam.Csv_to_AstraDb \
-Dexec.args="\
--astraToken=${ASTRA_TOKEN} \
--astraSecureConnectBundle=${ASTRA_SCB_PATH} \
--astraKeyspace=${ASTRA_KEYSPACE} \
--csvInput=`pwd`/src/test/resources/language-codes.csv"
- Check output data in Astra
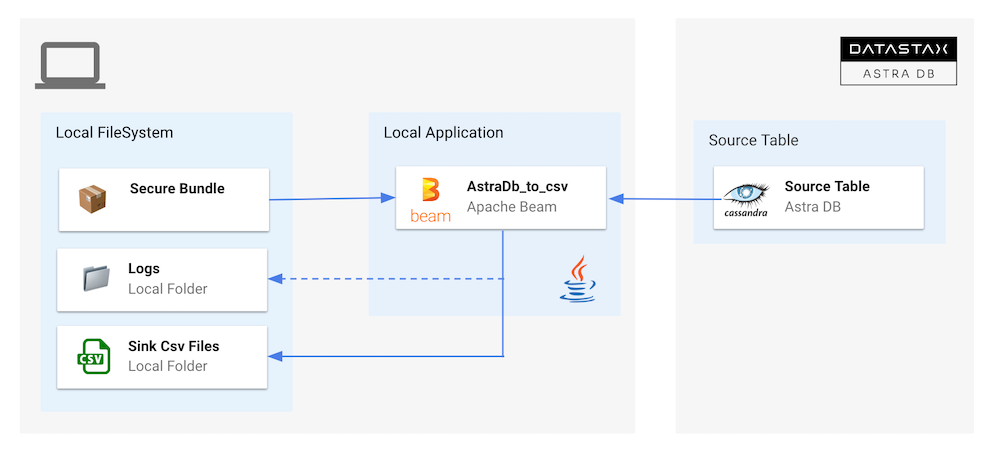
2. Export Table as CSV¶
In this flow a Cassandra table is exported as a CSV file. The mapping from table to csv row is done manually. The same objects are reused from
#1
- Access folder
- Setup Environment variables
# Database name (use with CLI)
export ASTRA_DB=<your-db-name>
# Keyspace name
export ASTRA_KEYSPACE=<your-keyspace-name>
# Path of local secure connect bundle
export ASTRA_SCB_PATH=<your-secure-connect-bundle>
# Astra Token starting by AstraCS:...
export ASTRA_TOKEN=<your-token>
- Run Beam pipeline
mvn clean compile exec:java \
-Dexec.mainClass=com.datastax.astra.beam.AstraDb_To_Csv \
-Dexec.args="\
--astraToken=${ASTRA_TOKEN} \
--astraSecureConnectBundle=${ASTRA_SCB_PATH} \
--astraKeyspace=${ASTRA_KEYSPACE} \
--table=languages \
--csvOutput=`pwd`/src/test/resources/out/language"
- Check output data in astra
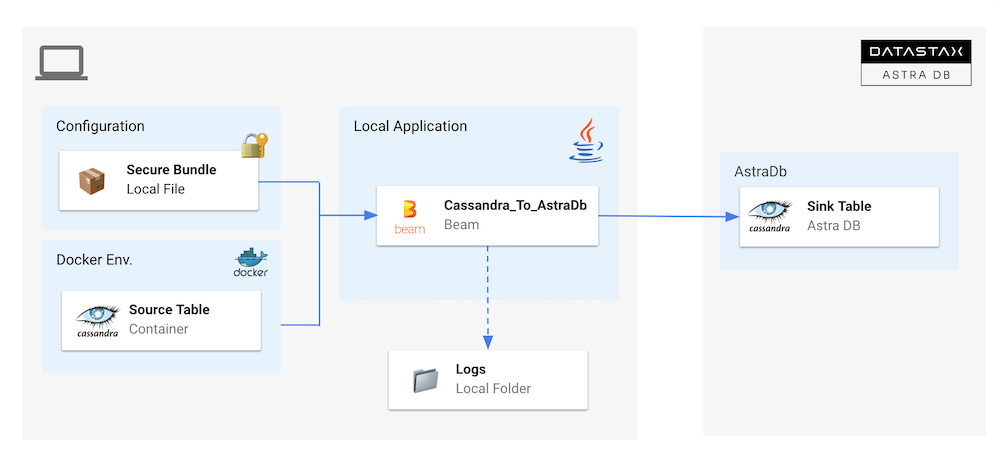
3. Import Cassandra Table¶
Similar to ZDM a cassandra Table is imported into Astra. We are reusing the same data model as before. Mapping is manual. We can note that Cassandra reading is operated with
CassandraIO(driver3x) where the load is done withAstraDbIO(drivers4x).
- Access folder
- Start Cassandra as a docker image with docker compose: Project propose a docker-compose to run Cassandra locally. Use
docker-composeto start the containers
- Wait a few seconds for Cassandra to Start. The following command give you the status of the container
- Validate Cassandra is ready: By connecting with
cqlshand displaying the datacenter.
docker exec -it `docker ps | \
grep cassandra:4.1.1 | \
cut -b 1-12` cqlsh -e "SELECT data_center FROM system.local;"
- Setup Env variables
export ASTRA_DB=<your-db-name>
export ASTRA_KEYSPACE=<your-keyspace-name>
export ASTRA_SCB_PATH=<your-secure-connect-bundle>
export ASTRA_TOKEN=<your-token>
- Run the pipeline: Keyspaces and Tables are created in local cassandra before starting the copy into Astra.
mvn clean compile exec:java \
-Dexec.mainClass=com.datastax.astra.beam.Cassandra_To_AstraDb \
-Dexec.args="\
--astraToken=${ASTRA_TOKEN} \
--astraSecureConnectBundle=${ASTRA_SCB_PATH} \
--astraKeyspace=${ASTRA_KEYSPACE} \
--cassandraHost=localhost \
--cassandraKeyspace=demo \
--cassandraTableName=languages \
--cassandraPort=9042 \
--tableName=languages"
- Check data in Cassandra with
cqlsh
docker exec -it `docker ps \
| grep cassandra:4.1.1 \
| cut -b 1-12` \
cqlsh -e "SELECT * FROM samples_beam.languages LIMIT 10;"
- Check data in Astra destination with
cqlsh(CLI)
4. Generative AI¶
This use cases is divided in 2 flows. In the first step we will import a CSV file as before mapping the CSV schema in destination table. Second flow will alter the table to add the embeddings vector and populate it after calling OpenAI Embedding API
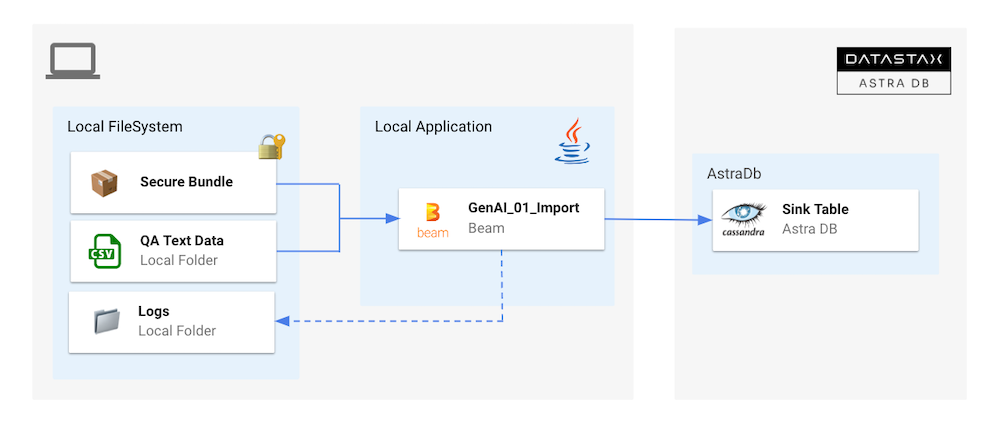
- Access folder
- Setup Env variables
export ASTRA_DB=<your-db-name>
export ASTRA_KEYSPACE=<your-keyspace-name>
export ASTRA_SCB_PATH=<your-secure-connect-bundle>
export ASTRA_TOKEN=<your-token>
- Import Data with first flow
mvn clean compile exec:java \
-Dexec.mainClass=com.datastax.astra.beam.genai.GenAI_01_ImportData \
-Dexec.args="\
--astraToken=${ASTRA_TOKEN} \
--astraSecureConnectBundle=${ASTRA_SCB_PATH} \
--astraKeyspace=${ASTRA_KEYSPACE} \
--csvInput=`pwd`/src/main/resources/fables_of_fontaine.csv"
A table is created with the following structure:
- Check output data in Astra
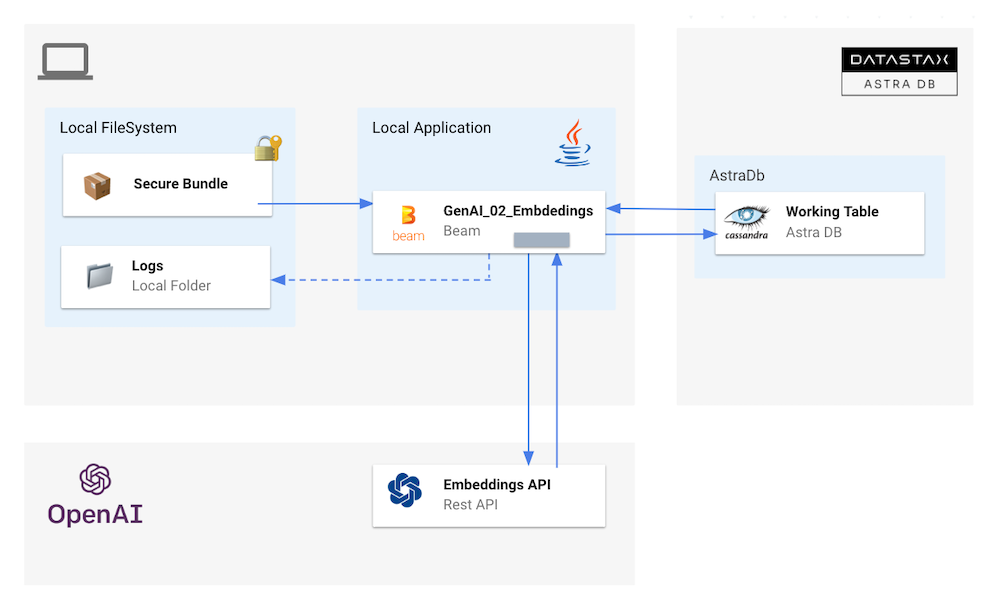
- Add extra environment variables
- Run pipeline
mvn clean compile exec:java \
-Dexec.mainClass=com.datastax.astra.beam.genai.GenAI_02_CreateEmbeddings \
-Dexec.args="\
--astraToken=${ASTRA_TOKEN} \
--astraSecureConnectBundle=${ASTRA_SCB_PATH} \
--astraKeyspace=${ASTRA_KEYSPACE} \
--openAiKey=${OPENAI_KEY} \
--table=${ASTRA_TABLE}"