• Spring

Spring makes programming Java quicker, easier, and safer for everybody. Spring’s focus on speed, simplicity, and productivity has made it the world's most popular Java framework. To get more information regarding the framework visit the reference website Spring.io.
Spring-Data is the module use to interact with Databases whereas Spring Boot is the runtime for microservices. In this page we detail how to setup both modules to interact with Astra.
1. Overview¶
1.1 Modules dependencies¶
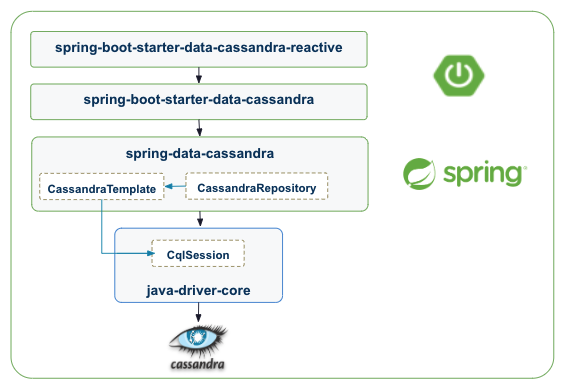
Spring is an ecosystem with dozens of modules. The component used to connect a Spring application to Astra (Cassandra) is Spring Data and especially Spring Data Cassandra. It relies on the DataStax native java cassandra drivers and only provides an abstraction with Spring concepts (templates, repository, Entities...)
The stateful object CqlSession is instantiated and injected in spring CassandraTemplate (aka CassandraOperations). From there, it is used either directly or injected in different CassandraRepository (specialization of Spring Data CrudRepository for Apache Cassandra™).
The configuration of spring-data-cassandra in Spring-Boot applications is simplified with the usage of starters. One is associated to the standard web stack and called spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra and the other is named spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra-reactive for the reactive stack.
1.2 Compatibility Matrix¶
In January 2019, the native Cassandra Drivers got an important, not backward compatible, upgrade. To get informations regarding Apache Cassandra™ support here is the Cassandra compatibility matrix.
Spring Data copes with the new generation of drivers starting with Spring data 3.x. Support of Astra was introduced in 2020 for all native versions (4.x and 3.x). This leads to the following table for minimal library versions for Astra Support:
| Drivers Release | Drivers Version | Spring-Data | Spring Boot |
|---|---|---|---|
Unified 4.x |
4.6.0 |
3.0.0.RELEASE |
2.3.0.RELEASE |
OSS 3.x |
3.8.0 |
Setup below table | 2.2.13.RELEASE |
DSE 2.x |
2.3.0 |
3.0.0.RELEASE |
2.3.0.RELEASE |
DSE 1.x |
1.9.0 |
Setup below table | 2.2 |
- Setup Spring Data 2.2.x (and before) to work with Astra
As stated in the matrix, even the latest Spring Data 2.2.13.RELEASE rely on cassandra-driver version 3.7.2 that where not yet compatible to Astra. To work with Astra you have to override the cassandra-drivers version as below.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra</artifactId>
<version>2.2.13.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.datastax.cassandra</groupId>
<artifactId>cassandra-driver-core</artifactId>
<version>3.11.2</version>
</dependency>
You can find here a sample project that uses Spring Boot version as old as 1.5.4.
- Setup Spring Data 2.2 (and before) to work with DataStax Enterprise (DSE)
Before 4.x and the unified drivers you have to use dse-java-driver-core to have access to enterprise features but also the be elligible for the support. To enable it
you need to exclude cassandra-driver-core and import dse-java-driver-core as show below
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra</artifactId>
<version>2.2.13.RELEASE</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.datastax.cassandra</groupId>
<artifactId>cassandra-driver-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.datastax.dse</groupId>
<artifactId>dse-java-driver-core</artifactId>
<version>1.9.0</version>
</dependency>
1.3 Rules and Pitfalls¶
- Define your own
CqlSessionbean (spring-data will find it !)
Spring Data Cassandra starters provide some dedicated keys in the configuration file application.yaml (spring.data.cassandra.*) but you do not get the complete list of options of the drivers. In the same way some super classes like AbstractCassandraConfiguration are provided where you can specify a few configuration properties but a limited set of keys are available.
- Do not use
findAll()
It can be tempting to use this method to test new repositories as no parameter is required - but this is dangerous. The default paging mechanism is skipped and this method will retrieve every single record of the table. As such, it would perform a full scan of the cluster (pick data for each node) that (1) would be slow and (2) could lead to OutOfMemoryException as Cassandra Tables are expected to store billions of records.
- Do not use
@AllowFiltering
This annotation (some for associated CQL Statement) is limited for the use cases where (1) you provide the partition key AND (2) you know your partition size is fairly small. In 99% of the cases the need of this annotation (or ALLOW FILTERING in the CQL) is a sign of a wrong data model: your primary key is invalid and you need another table to store the same data (or eventually to create a secondary index).
- Do not rely (only) on Spring Data to create your schema
SDC provide a configuration key spring.data.cassandra.schema-action: CREATE_IF_NOT_EXISTS that proposes to create the Cassandra Tables based on your annotated beans. It is NOT a good idea. Indeed, it could lead to wrong data model (cf next point) but also it does not give access to fine grained properties like COMPACTION and TTL that might be different in development and production. Let a Cassandra Administrator reviews your DDL scripts and updates them for production.
- Data Model First, Entities second
With the JPA (entity, repository) methodology, you are tempting to reuse the same entities and repositories to perform multiple queries against the same table. Most new requests will be not valid as you will not request using the primary key. You can be tempting to create a secondary index or use allow filtering; WRONG !. The good practice is to CREATE ANOTHER TABLE, ANOTHER ENTITY and ANOTHER REPOSITORY - and even if data stored is the same. With Cassandra 1 query = 1 table (mostly).
CassandraRepositoryprobably cannot implement it all
With real-life applications you might probably need to go back to the CqlSession and execute custom fine-grained queries (Batches, TTL, LWT...). The interfaces and CassandraRepostiory would not be enough. The class SimpleCassandraRepository is an abstract class (not interface0 you can inherit from that give you access to the CqlSession and execute your queries as you like, it is a good trade off.
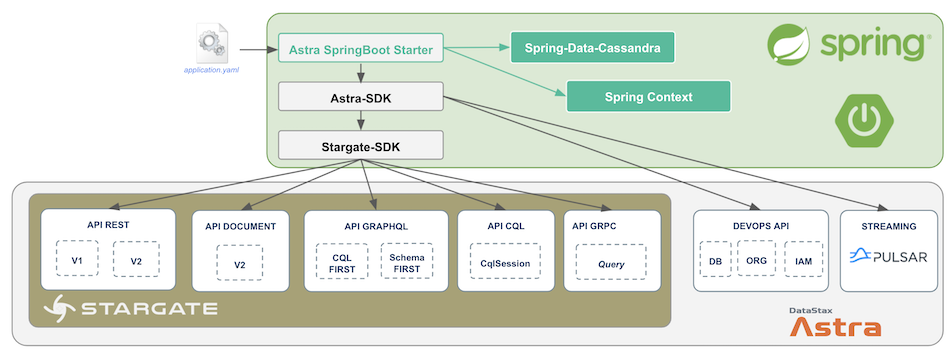
2. Astra Spring Boot Starter¶
2.1 Introduction¶
The Astra Spring Boot Starter will configure both Astra SDK and Spring Data Cassandra to work with AstraDB. Configuration keys are provided in application.yaml like any spring applications with a dedicated prefix astra.*. The starter will initialize any beans you would need (AstraClient, CqlSession, StargateClient) to use every interfaces exposes by Astra. Not all are activated by default though, you want to initialize only what you need.
2.2 Project Setup¶
Prerequisites [ASTRA]¶
- You should have an Astra account
- You should Create an Astra Database
- You should Have an Astra Token
Prerequisites [Development Environment]¶
- You should install Java Development Kit (JDK) 8: Use the reference documentation to install a Java Development Kit, Validate your installation with
- You should install Apache Maven: Use the reference documentation and validate your installation with
Setup Project¶
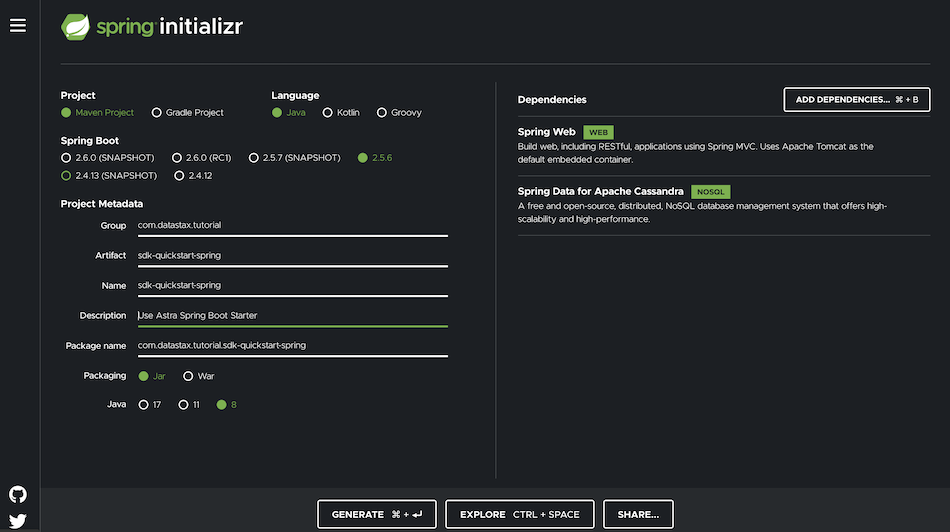
- Create your project with Spring Initializr. Dependencies needed are
webanddata-cassandrabut we did the work for you if you click the template link
| Property | Value | Property | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| groupId | com.datastax.tutorial |
package | com.datastax.tutorial |
| artifactId | sdk-quickstart-spring |
description | Sample Spring App |
| name | sdk-quickstart-spring |
dependencies | Spring Web and Spring Data for Cassandra |
| packaging | JAR |
Java Version | 8 or 11 |
-
Import the application in your favorite IDE but do not start the application immediately.
-
Add the latest version of starter as a dependency in
pom.xmlof
astra-spring-boot-starterin the project.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.datastax.astra</groupId>
<artifactId>astra-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>0.3.4</version>
</dependency>
2.3 Code and Configuration¶
- Change the main class with the following code, we are leveraging on the unique
AstraClientto interact with multiple interfaces.
@RestController
@SpringBootApplication
public class SdkQuickstartSpringApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SdkQuickstartSpringApplication.class, args);
}
// Provided by the Starter
@Autowired
private AstraClient astraClient;
// Spring Data using the CqlSession initialized by the starter
@Autowired
private CassandraTemplate cassandraTemplate;
@GetMapping("/api/devops/organizationid")
public String showOrganizationId() {
return astraClient.apiDevopsOrganizations().organizationId();
}
@GetMapping("/api/spring-data/datacenter")
public String showDatacenterNameWithSpringData() {
return cassandraTemplate.getCqlOperations()
.queryForObject("SELECT data_center FROM system.local", String.class);
}
@GetMapping("/api/cql/datacenter")
public String showDatacenterNameWithSpringData() {
return astraClient.cqlSession()
.execute("SELECT data_center FROM system.local")
.one().getString("data_center");
}
}
Rename src/main/resources/application.properties to src/main/resources/application.yaml. This step eases the configuration with hierarchical keys. Populate application.yaml with the following content and replace the values with expected values (how to retrieve the values are explained in the Quickstart Astra
astra:
# Allow usage of devops and Stargate apis
api:
application-token: <your_token>
database-id: <your_database_id>
database-region: <your_database_region>
# Connectivity to Cassandra
cql:
enabled: true
download-scb:
enabled: true
driver-config:
basic:
session-keyspace: <your_keyspace>
- Start the application
- Access the resources we created
- Get your Organization ID:
http://localhost:8080/api/devops/organizationid - Get your Datacenter Name (Spring-data):
http://localhost:8080/api/spring-data/datacenter - Get your Datacenter Name (cql):
http://localhost:8080/api/cql/datacenter
3. Spring Data Cassandra¶
3.1 Project Setup¶
Prerequisites [ASTRA]¶
- You should have an Astra account
- You should Create an Astra Database
- You should Have an Astra Token
- You should Have downloaded your Cloud Secure Bundle
Prerequisites [Development Environment]¶
- You should install Java Development Kit (JDK) 8: Use the reference documentation to install a Java Development Kit, Validate your installation with
- You should install Apache Maven: Use the reference documentation and validate your installation with
Setup Project¶
- Create a Spring Boot application from the initializer and add the
spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra</artifactId>
</dependency>
3.2 Code and Configuration¶
- Setup the configuration file
application.yaml
spring.data.cassandra:
keyspace-name: myks
username: myClientId
password: myClientSecret
schema-action: CREATE_IF_NOT_EXISTS # for dev purpose
request:
timeout: 10s
connection:
connect-timeout: 10s
init-query-timeout: 10s
datastax.astra:
# You must download it before
secure-connect-bundle: /tmp/secure-connect-bundle.zip
- Create a dedicated configuration bean to parse
datastax.astra
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "datastax.astra")
public class DataStaxAstraProperties {
private File secureConnectBundle;
// Getter and Setter omitted
}
- Define a bean of
CqlSessionBuilderCustomizerto add thisCloudSecureBundle
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DataStaxAstraProperties.class)
public class SpringDataCassandraApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringDataCassandraApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public CqlSessionBuilderCustomizer sessionBuilderCustomizer(DataStaxAstraProperties astraProperties) {
Path bundle = astraProperties.getSecureConnectBundle().toPath();
return builder -> builder.withCloudSecureConnectBundle(bundle);
}
}
